Tables
Rapid uses a database to store information.
At the risk of oversimplifying: you can think of a database like a collection of files or spreadsheets that are connected to each other.
In this section, we will examine the concept of a Table (what it is, and why it's important).
What is a Table?
Most databases use tables to organise and store information.
In Rapid, you can open tables to view their information.
Tables are divided into vertical columns (similar to a spreadsheet). This allows all the data placed onto a table to be organised.
Tables contain horizontal rows. These are also referred to as items.
An Example Table
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Item 1 | Data | Data | Data |
| Item 2 | Data | Data | Data |
| Item 3 | Data | Data | Data |
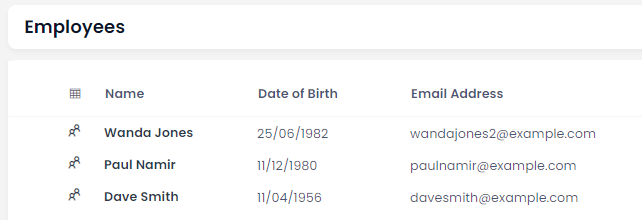
If we wanted to create a table that records an employee's name, date of birth, and email address, we could build a table like so:
Why are Tables Important?
A table is the simplest way to convey a lot of information.
A table allows us to categorise that information.
For example, the Contacts table is where I store my company's external Contacts. So, the data on this table must be a type of Contact. I cannot (for instance) store my favourite ice cream flavours on the Contacts table.
If you have a Rapid Business site installed, you will see tables such as: Tasks, Assets, Employees, Quotes, Invoices, Projects, etc. Each of these table names describes the type of data they contain.
How do I find the data I need?
In the sidebar you will find most of the tables that are packaged with Rapid business. These tables are grouped into menu folders (e.g. Finance, Human Resources, WHS).
You can also use views to help you find the relevant information on a table. We will discuss views on the next page.
Further Reading
- A one-page summary that explains table functionality further
- The complete documentation on tables